Suppose, we need to identify, from the given image

whether an image is a “Winter Family Photo” or “Not a Winter Family Photo”.
Step 1: Identify the Goal (Target Variable)
Target / Output class:
- Winter Family Photo
- Not a Winter Family Photo
This is a binary classification problem.
Step 2: Identify the Features (Attributes)

From the given images, we consider the following features:
- Cartoon Character? (Yes / No)
- Winter? (Yes / No) → snow, jackets, winter background
- More than 1 person? (Yes / No)
These are independent features used to make decisions.
Step 3: Build the Decision Tree (Top-Down Approach)
Root Node Selection using Information GainIn decision trees (ID3 algorithm),
👉 Feature with the highest Information Gain is chosen as the root node.
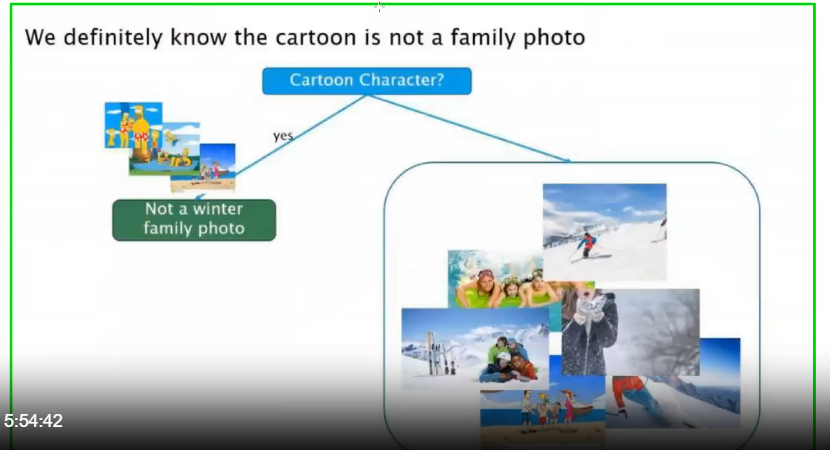
1️⃣ First Split: Cartoon Character?
- Cartoons are not real family photos
- This split removes many incorrect images immediately
- Highest Information Gain
So, the root node is:
Cartoon Character?
If YES → Not a winter family photo
If NO → Continue splitting
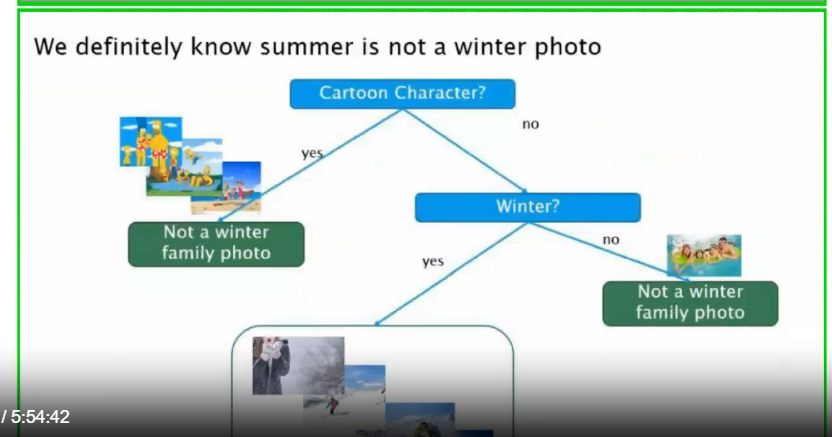
2️⃣ Second Split: Winter?
For non-cartoon images:
Winter?
If NO → Not a winter family photo (summer images)
If YES → Continue splitting
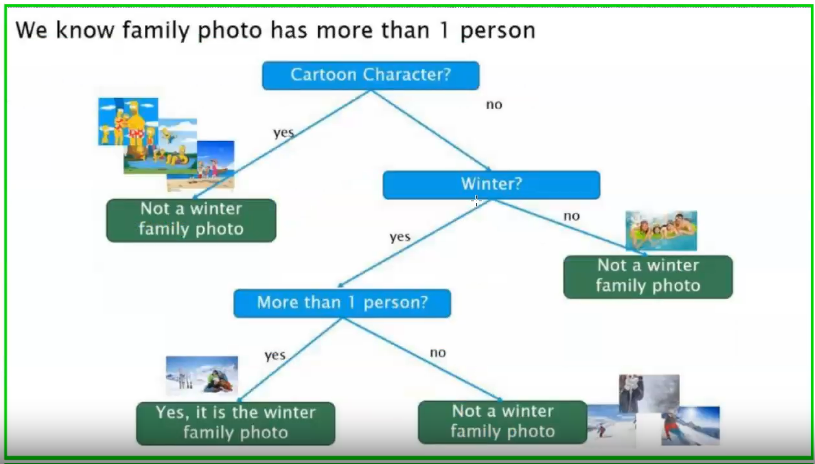
3️⃣ Third Split: More than 1 person?
Because a family photo must contain more than one person:
More than 1 person?
YES → ✔ Winter family photo
NO → ✖ Not a winter family photo


Step 4: Role of Information Gain (Concept Explanation)
What is Information Gain?
Information Gain = Reduction in Entropy
- Measures how well a feature separates the data
- Higher Information Gain → Better feature for splitting
Why “Cartoon Character?” is Chosen First?
Splitting by cartoon images immediately classifies many images
Reduces uncertainty the most
Hence, it has the highest Information Gain
Other features like Winter and Number of persons give less gain initially, so they appear
lower in the tree.
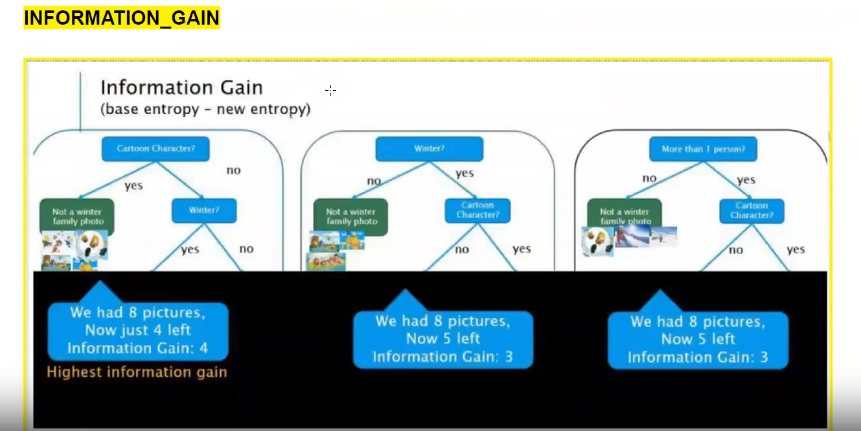
What the image shows
The image compares three possible features to decide which one should be the root node of a
decision tree using Information Gain.
- Total images (dataset) = 8 pictures
- Goal: Select the best feature that separates the data most clearly
- Information Gain = Base Entropy − New Entropy
Step 1: Initial Situation (Base Entropy)
At the start:
We have 8 mixed pictures
Some are winter family photos
Some are not
Because the data is mixed, entropy is high (high uncertainty).
Step 2: Try Different Splits (Three Features)
The image shows three candidate features:
1️⃣ Cartoon Character?
2️⃣ Winter?
3️⃣ More than 1 person?
Each feature is tested to see how much it reduces uncertainty.
Case 1: Split using Cartoon Character?
After splitting:
o Cartoon images are immediately classified as Not a winter family photo
o Remaining images = 4
Uncertainty is reduced a lot
Result shown in image:
We had 8 pictures
Now just 4 left
Information Gain = 4 (Highest)
This means Cartoon Character? separates the data best.
Case 2: Split using Winter?
After splitting:
o Some images are still mixed
o Remaining images = 5
More uncertainty remains compared to Case 1
Result shown in image:
We had 8 pictures
Now 5 left
Information Gain = 3
Good split, but not the best.
Case 3: Split using More than 1 person?
After splitting:
o Still mixed images in both branches
o Remaining images = 5
Less effective in reducing uncertainty
Result shown in image:
We had 8 pictures
Now 5 left
Information Gain = 3
Same gain as Winter?, but still lower than Cartoon Character?.
Step 3: Selecting the Root Node
Rule:
Feature with the highest Information Gain becomes the root node
From the image:
Cartoon Character? → IG = 4
Winter? → IG = 3
More than 1 person? → IG = 3
Final Decision:
Cartoon Character? is selected as the root node
What This Image Teaches
Information Gain measures how much uncertainty is reduced
Bigger reduction = better feature
Decision trees always choose the feature with maximum Information Gain
This is how the ID3 algorithm works
