Numerical example of decision tree using ID3
Suppose, we have, 2 features
Feature 1,
(Feature = F1)
Feature
Explanation
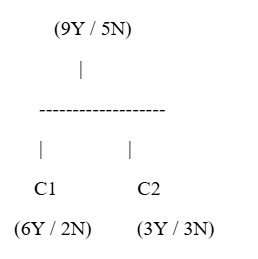
Root Node:
Feature → 9 Yes / 5 No
First Split (C1):
6 Yes / 2 No → More pure node
Second Split (C2):
3 Yes / 3 No → Highly impure node
Step 1: Entropy of Root Node
Entropy Formula
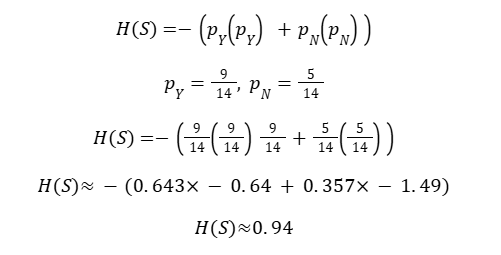
Root node is impure
Step 2: Entropy of Child Node C1 (6Y / 2N)
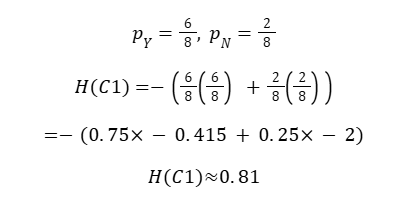
More pure node
Step 3: Entropy of Child Node C2 (3Y / 3N)
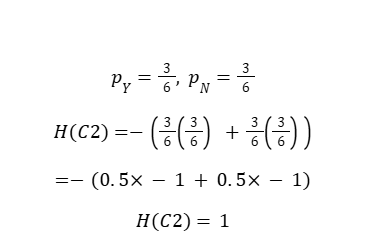
Highly impure node (maximum entropy)
Information gain
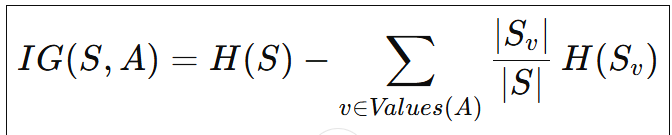
Where:
- → Entire dataset (parent node)
- → Attribute / feature used for splitting
- → All possible values of attribute
- → Subset of where attribute
- → Total number of samples
- → Number of samples in subset
- → Entropy of parent node
→ Entropy of child node
Step 4: Weighted Entropy After Split
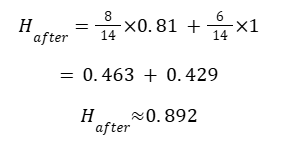
Step 5: Information Gain
Formula
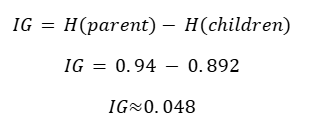
(Feature 2)
Root (S): 9Y / 5N → Total = 14
Child C1: 5Y / 1N → Total = 6
Child C2: 4Y / 4N → Total = 8
Step 1: Entropy of Root Node
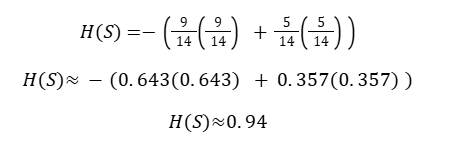
Step 2: Entropy of Child C1 (5Y / 1N)
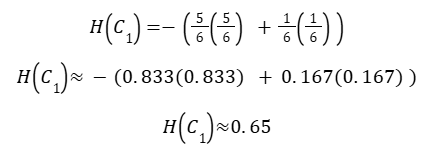
Step 3: Entropy of Child C2 (4Y / 4N)
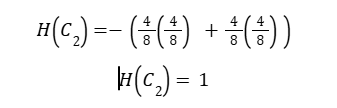
Step 4: Weighted Entropy After Split
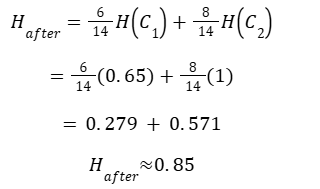
Step 5: Information Gain for Feature 2

Feature 1
- Root: 9Y / 5N
- Children:
- C1 → 6Y / 2N
- C2 → 3Y / 3N
Feature 2
Root: 9Y / 5N
Children:
C1 → 5Y / 1N
C2 → 4Y / 4N
Comparison Table
| Feature | Information Gain |
| Feature 1 | ≈ 0.05 |
| Feature 2 | ≈ 0.09 |
Final Conclusion (ID3 Decision)
ID3 algorithm always selects the feature with the highest Information Gain as the root
node.
Since:
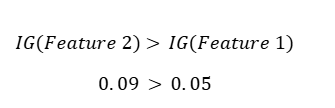
Feature 2 is selected as the ROOT FEATURE
