CART selects the split with the LOWEST weighted Gini index.
For example
Parent node: 20 samples, classes = 10 / 10.
Left child: 14 samples, classes = 8 / 6.
Right child: 6 samples, classes = 2 / 4.
We will compute:
Gini of parent
Gini of left child
Gini of right child
Weighted Gini after the split
Gini decrease (how much impurity the split removed)
Step 1:
Parent Gini

So
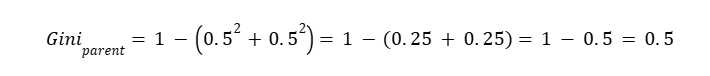
Parent Gini = 0.5
Step 2:
2) Left child Gini (14 samples: 8 and 6)
Proportions:
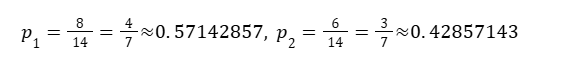
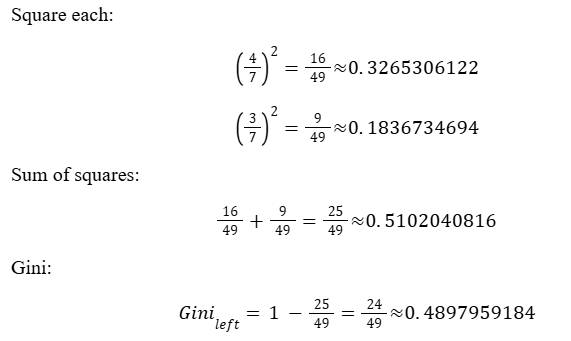
Step 3:
3) Right child Gini (6 samples: 2 and 4)
Proportions:
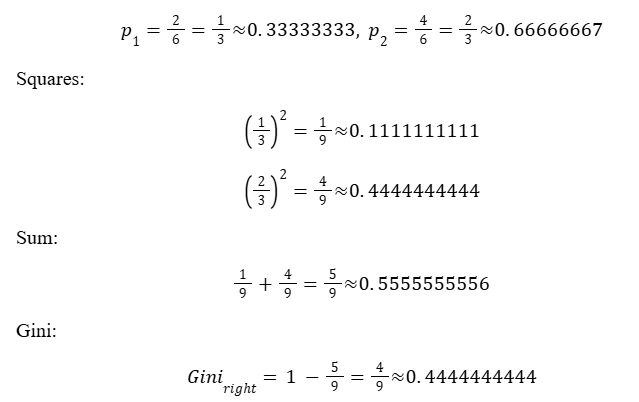
Step 4:
4) Weighted Gini after the split
CART binary split weighted Gini:
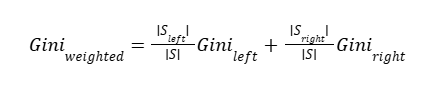

Weighted Gini ≈ 0.4761904762
Step 5:
5) Gini decrease (how much impurity reduced)
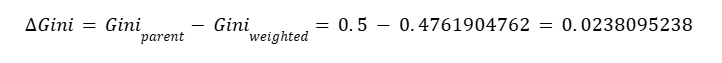
Gini decrease ≈ 0.0238095238 (≈ 0.024)
Final summary
Parent Gini = 0.5
Left child Gini ≈ 0.4897959184
Right child Gini ≈ 0.4444444444
Weighted Gini after split ≈ 0.4761904762
Gini decrease ≈ 0.0238095238
Interpretation: the split reduces impurity slightly (by ≈ 0.024). In CART we compare this decrease with other candidate splits and pick the split with the largest decrease.
