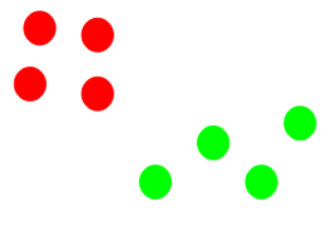
Suppose we have 8 data points on a graph.
Our goal is to group these points into clusters using the K-Means algorithm.

Step 1: Choose the Number of Clusters (K)
- First, we decide how many clusters we want.
- Let us choose K = 2, meaning:
- We want to divide the 8 points into 2 groups.
👉 This value of K is chosen before running the algorithm.
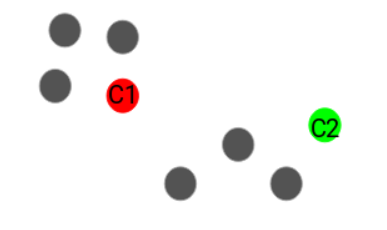
Step 2: Select K Random Points as Initial Centroids
- Since K = 2, we randomly select 2 points from the dataset.
- These points act as the initial centroids.
- In the diagram:
- One centroid is shown in red
- The other centroid is shown in green
👉 At this stage, centroids may not be in the correct position. They are only a starting guess.
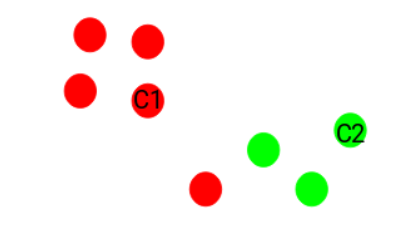
Step 3: Assign Each Point to the Nearest Centroid
- For each of the 8 data points:
- Calculate the distance from the red centroid
- Calculate the distance from the green centroid
- Assign the point to the cluster whose centroid is closest.
Result:
- Points closer to the red centroid → Red cluster
- Points closer to the green centroid → Green cluster
👉 This forms the first set of clusters.
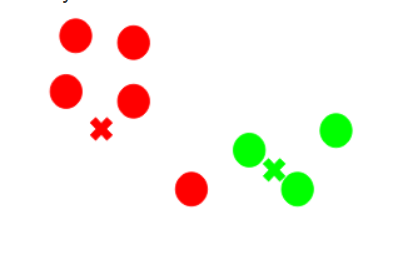
Step 4: Recompute the Centroids
- Now, for each cluster:
- Take all points belonging to that cluster
- Calculate their mean (average position)
- The mean position becomes the new centroid.
In the diagram:
- Red and green crosses represent the new centroids
👉 Centroids move toward the center of their respective clusters.
Step 5: Repeat Steps 3 and 4 (Iterations)
- Using the new centroids:
- Again assign points to the nearest centroid
- Again recompute the centroids
👉 One complete cycle of:
- Assigning points
- Updating centroids
is called one iteration.
This process is repeated multiple times.