Think of Machine Learning like teaching a child to recognize fruits.
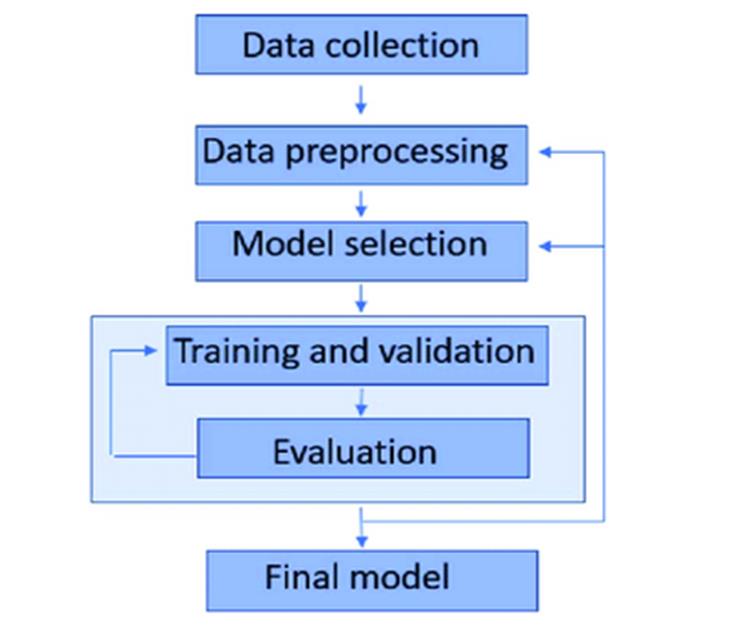
Just like humans learn step-by-step, machines also learn using a sequence of steps. These steps form the Machine Learning Workflow. Figure depicts Machine Learning Workflow.
Step 1: Data Collection- Collect Data (Raw Data)
This is the first and most important step.
Every ML model starts with data
Meaning:
Gather the information the machine will learn from.
Example:
If the goal is to identify fruits, the data could be many images of apples, bananas, grapes.
- Student marks data
- Email spam dataset
- Patient medical records
- Product reviews
Data is like the study material for the machine. Without study material, learning cannot start.
Step 2: Data Preprocessing (Cleaning the Data) – Preprocess & Clean Data
Raw data is usually messy, incomplete, or inconsistent.
Meaning:
Real-world data is messy.
We must clean it before giving it to the model.
Fix mistakes in the data, remove noise, and make everything clean and uniform.
For example,
🔹 1. Handling Missing Values
Explain like this:
“Sometimes, some information is not available in data.”
Example table:
| Student | Marks |
| A | 85 |
| B | ❌ |
| C | 78 |
Ask students:
“Can a model work with blank values?”
Answer: ❌ NO
What we do:
- Remove that row
- OR fill missing value with:
- Average marks
- Most common value
Say:
“We either remove missing data
or fill it with a reasonable value.”
🔹 2. Removing Duplicate Records
“If the same student’s record appears twice,
the model thinks there are two students.”
Example:
| Student | Marks |
| A | 80 |
| A | 80 |
Say:
“This gives wrong importance to some data.”
Solution:
- Keep only one copy
- Delete duplicates
Example:
Removing blurry images, correcting wrong labels, resizing pictures, removing duplicate entries.
Simple explanation:
Before the machine studies, we clean the notes so it doesn’t get confused.
3. Choose a Model
Different tasks need different models.
Meaning:
Select the type of machine learning algorithm suitable for the problem.
Example:
For fruit classification, you might use a decision tree, neural network, etc.
Choosing a model is like choosing the right tool—scissor for paper, knife for fruit.
- Linear Regression
- Decision Tree
- KNN
- Naive Bayes
- SVM
STEP 4: Training and Validation
What it means:
Teaching the model using data and checking its learning.
What is Model Training?
Model Training is the process of teaching a machine learning model using past data so that it can learn patterns and make correct predictions in the future.
During training, the model is given input data and correct answers (labels). The model makes predictions, compares them with the actual answers, and improves itself by adjusting its internal values (called weights).
This step internally includes Train–Test Split.
What happens inside this step:
- Dataset is divided into:
- Training data (for learning)
- Validation/Test data (for checking)
- Model learns patterns from training data
- Validation checks if learning is correct
training data is like studying,
validation is like practice tests.
In very simple words:
Model training means making the machine learn from examples.
for example:
Student Pass / Fail Prediction
Step 1: Training Data (Past Records)
We give the model old student data:
| Marks | Result |
| 80 | Pass |
| 35 | Fail |
| 60 | Pass |
| 40 | Fail |
This is called training data.
The model looks at this data and starts learning a pattern:
Higher marks → Pass
Lower marks → Fail
This learning process is Model Training.
Validation (Checking the Learning)
Now we give different student data (not used in training):
| Marks | Actual Result |
| 70 | Pass |
| 38 | Fail |
This is validation data.
Here we check:
- Did the model learn correctly?
- Is it predicting properly?
STEP 5: Evaluation
What it means:
Measuring how well the trained model performs.
Explain clearly:
“Now the model is tested on unseen test data.”
This is where performance metrics are calculated:
- Accuracy
- Precision
- Recall
- F1-score
All performance metrics are calculated on TEST DATA,
not on training data.
6. Deploy the Model
Once the model works well, use it in the real world.
Meaning:
Put the model into an application so others can use it.
Example:
A mobile app that identifies fruits in real time.
Simple explanation:
“This is when the machine starts using its knowledge to help people.”
7. Model Inferencing
What is Model Inferencing?
Model Inferencing means using a trained and deployed model to make predictions on new, unseen data.
In simple words:
Inferencing = Asking the trained model to give answers.
After a model is trained and deployed, it is ready to work in the real world. Whenever new input is given, the model processes it and produces an output — this process is called inferencing.
Think of this sequence:
- Training → Teaching the model
- Deployment → Placing the model in an application
- Inferencing → Using the model
So,
Deployment makes the model available.
Inferencing actually uses the model.
Easy Analogy
- Training → Studying from textbooks
- Deployment → Getting a job
- Inferencing → Doing daily work
You don’t start working just by studying — you work after you get the job
Example 1: Student Pass / Fail Prediction
Step 1: During Training
We give the model past student data:
| Marks | Result |
| 80 | Pass |
| 35 | Fail |
| 60 | Pass |
| 40 | Fail |
The model learns a pattern like:
“Higher marks → Pass, lower marks → Fail”
Step 2: Deployment
Now this trained model is added to a college software system.
Step 3: Inferencing (Real Use)
Now a new student’s marks are entered:
Marks = 72
The model thinks using what it learned and predicts:
Output: Pass
This prediction process is called model inferencing.
Example 2: Email Spam Detection
- Model is trained using old emails (spam / not spam)
- Model is deployed in Gmail
- A new email arrives
- Model predicts: Spam or Not Spam
That prediction = Inferencing
Summary
Collect Data: Get the study material
- Clean Data: Make the material neat
- Choose Model: Pick the right learning method
- Train Model: Machine learns
- Evaluate Model: Check performance
- Deploy Model: Use it in real world
- Model Inferencing (Prediction on new data)
