Okay, now that we’ve met our single artificial neuron — the perceptron — let’s see what happens when many of them start working together.
Think of it like a group project: one neuron alone can do only simple tasks, but when hundreds of them join forces, they can solve complex problems like recognizing faces, understanding speech, or even driving cars!
To solve complex problems such as image recognition, speech recognition, and language translation, multiple neurons are connected together to form an Artificial Neural Network (ANN).
Definition
An Artificial Neural Network (ANN) is a computational model inspired by the human brain, consisting of interconnected artificial neurons arranged in layers.
These neurons work together to learn patterns from data by adjusting weights during training.
An ANN is usually organized into three main types of layers:
- Input Layer
This is where the network receives data.
Each node (or neuron) in this layer represents one feature from the dataset.
Example: If you are predicting whether an image is of a cat or dog, each pixel’s value from the image becomes an input. - Hidden Layer(s)
This is the brain of the network.
It processes the inputs, detects patterns, and learns relationships between data.
The more hidden layers a network has, the deeper it becomes — that’s why we call them Deep Neural Networks (DNNs).
Example: In our cat-dog image, the first hidden layer might detect edges, the next one eyes and ears, and another might detect fur patterns. - Output Layer
This is where the final decision is made.
Example: Output layer might say — “ 90% Dog, 10% Cat.”
Each connection has a weight (importance), and the network learns by adjusting those weights .
Following fig shows Weights and Bias in Artificial neural network
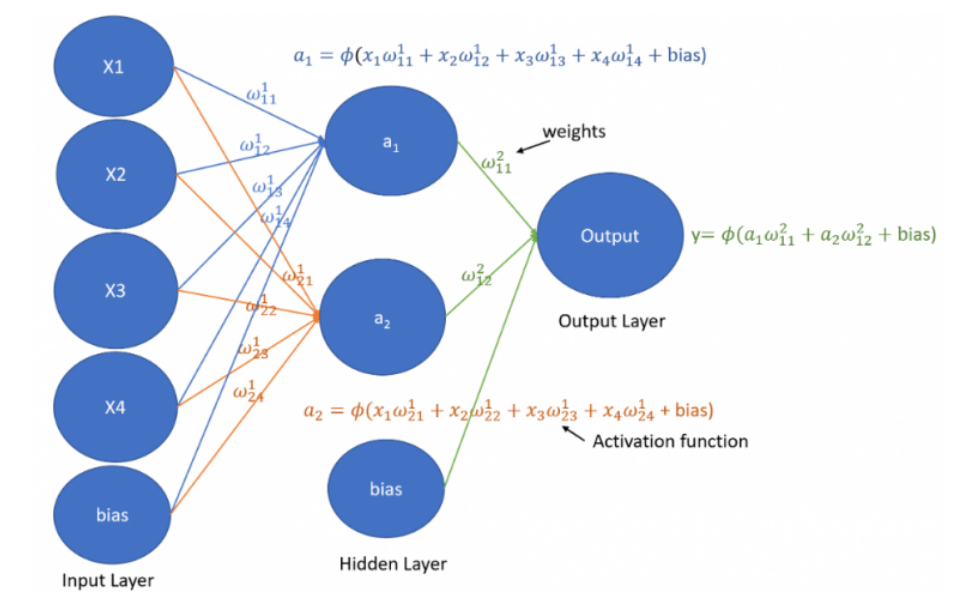
The working of an Artificial Neural Network (ANN) can be understood as a step-by-step process in which the network receives input data, makes a prediction, checks the error, and learns by correcting its mistakes. The following steps explain the working of an ANN.
1️⃣ Input
- The ANN first receives input data.
- Each input is a feature of the problem.
Example:
Marks, height, image pixels, or yes/no features.
👉 Inputs are given to the input layer.
2️⃣ Forward Propagation (Guessing Stage)
- Inputs move forward through the network:
- Input layer → Hidden layer → Output layer
- In each neuron:
- Inputs are multiplied by weights
- Bias is added
- Activation function is applied
👉 The network makes a guess.
3️⃣ Output
- The output layer gives the final prediction.
- This can be:
- 0 or 1 (classification)
- A value (regression)
👉 This is what the network thinks is the answer.
4️⃣ Backward Propagation (Learning Stage)
- The output is compared with the correct answer.
- Error is calculated.
- The error is sent backward through the network.
- Weights and bias are adjusted to reduce the error.
👉 The network learns from its mistake.
5️⃣ Repeat (Training)
- Steps 1 to 4 are repeated many times.
- Each time, the error becomes smaller.
- The prediction becomes more accurate.
Final Understanding (One-line)
Input → Guess → Check → Correct → Repeat
In this way, an Artificial Neural Network learns from data and improves its output step by step.
“Forward propagation is guessing, backward propagation is correcting.”
