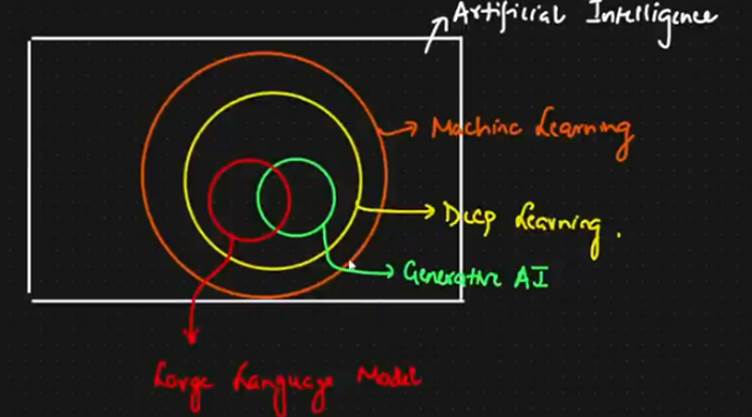
“Everything inside this box is part of Artificial Intelligence —
which means any computer system that can think, learn, or make decisions like a human.”
Examples:
- Chess-playing programs
- Chatbots
- Face recognition on your phone
- Self-driving cars
AI is the broadest concept — it includes all smart machines.
Inside AI — Machine Learning (ML)
Now move to the orange circle.
Machine Learning is a part of AI that doesn’t just follow rules —
it learns from data and experience.”
You show the computer 1000 pictures of cats and dogs —
it learns patterns and then predicts which is which.
Inside ML — Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning is a special kind of Machine Learning that uses neural networks,
which are inspired by how our brain works.
Deep Learning = learning using neural networks.
It’s the reason modern AI (like ChatGPT) became so powerful.
Deep Learning models
Deep Learning → Two Types:
1. Discriminative → Classify or Predict (e.g., Cat vs Dog)
2. Generative → Create New Data
→ (a) Language Models → ChatGPT, Bard
→ (b) Image Models → DALL·E, Midjourney
There are two main types of Deep Learning models:
Discriminative Models and Generative Models.
Deep Learning models can do two kinds of work —
either understand existing data or create new data.
These are called Discriminative and Generative models.
What are Discriminative Models?
Definition :
A Discriminative model learns to classify or predict something based on labeled examples.
“It’s like a teacher showing the AI pictures of cats and dogs,
and the AI learns to tell which is which.”
Task type: Classification or Prediction
(e.g., Is this photo a cat or a dog?)
Dataset: Labeled dataset
→ Each example already has a known answer.
What it does:
Learns the boundaries between classes — e.g., “this side is cat,” “that side is dog.”
Examples of Discriminative Models
| Task | Example |
| Image classification | CNN classifying cats vs dogs |
| Spam detection | Classify email as Spam or Not Spam |
| Handwriting recognition | Identify digits (0–9) |
Discriminative models are like exam checkers —
they decide which category something belongs to.
What are Generative Models?
Definition :
A Generative model learns the patterns in data and uses them to generate new data similar to what it learned.
“Instead of just telling whether a picture is a cat or dog,
a generative model can actually create a new picture of a cat or a dog!”
Task type: Data Generation
(e.g., generate text, images, audio, or video)
Dataset: Trained on some dataset (doesn’t just classify, it learns the distribution of the data).
What it does:
Learns how the data is structured, then produces new, similar data.
Examples of Generative Models
| Task | Example |
| Text generation | ChatGPT predicting next word in a sentence |
| Image generation | DALL·E or Midjourney creating pictures |
| Voice synthesis | AI generating human-like voices |
| Music generation | AI composing new melodies |
Generative models are like creative artists —
they learn from existing art and create something new.
Key difference
| Feature | Discriminative Model | Generative Model |
| Goal | Classify or Predict | Create or Generate |
| Input Data | Labeled (has correct answers) | Can be unlabeled (just examples) |
| Output | A label or class | New data or content |
| Example | “Is this email spam?” | “Write a new email like this one.” |
| Real Example | Image classifier, Sentiment analyzer | ChatGPT, DALL·E, Deepfake generator |
| Analogy | Judge (decides what it is) | Artist (creates something new) |
example
| Task | Discriminative AI | Generative AI |
| Input | Cat & dog images labeled as “cat” or “dog” | Many images of cats & dogs (no labels needed) |
| Goal | Learn to predict: “Is it cat or dog?” | Learn to create new images of cats or dogs |
| Output | “Cat” or “Dog” | A new, never-seen-before cat image 🐱 |
The discriminative model is a classifier,
the generative model is a creator.
Discriminative Models: Learn to separate or classify data (e.g., cat vs dog).
Generative Models: Learn to create new data (e.g., generate a cat image or text).
Two Types of Generative Models
(A) Generative Language Models
Definition:
“These models work with text and language — they generate new sentences, stories, or answers.”
Example:
ChatGPT, Google Bard, Gemini, Claude
How they work:
They learn from a massive amount of text — books, articles, code, etc.
Then they predict the next word in a sentence again and again — that’s how they “write.”
Example in simple words:
Input: “Artificial Intelligence is”
Output: “the simulation of human intelligence by machines.”
Generative Language Model → creates new text.
(B) Generative Image Models
Definition:
“These models work with images — they create new pictures, designs, or art.”
Example:
DALL·E
How they work:
They learn from millions of pictures and descriptions.
Then, when you type ‘a dog wearing glasses’, they generate a completely new image of that — never seen before.
Generative Image Model → creates new images.
Comparison Table
| Type | What it does | Example |
| Discriminative Model | Classifies or predicts categories | “Is this a cat or dog?” |
| Generative Language Model | Creates new text | ChatGPT writing an essay |
| Generative Image Model | Creates new pictures | DALL·E generating artwork |
Real-Life Example
If you upload your selfie and ask an AI to tell whether you’re smiling or not —
that’s Discriminative AI.
If you ask it to draw you as a cartoon —
that’s Generative AI.
And if you ask it to write your Instagram bio —
that’s a Generative Language Model.
Summary
| Concept | Function | Example |
| Discriminative Models | Classify and predict | Image classification, Spam detection |
| Generative Models | Create new data | ChatGPT, DALL·E |
| Generative Language Models | Generate text | ChatGPT, Gemini |
| Generative Image Models | Generate images | DALL·E, Midjourney |
Inside DL — Generative AI (Green Circle)
how Generative AI (GenAI) works
Generative AI takes some data as input, learns patterns from it, and then creates new data or content as output.
So it has three stages:
DATA → GenAI Model → New Content
or
Input → Process → Output
Step 1 – Input: DATA
Data (Input)
“This is the information the AI is trained on.”
“Generative AI learns from unstructured content — that means text, images, audio, or videos that are not organized in tables or rows.”
Examples of unstructured content:
- Text (books, articles, Wikipedia pages)
- Images (photos, art)
- Audio (music, speech)
- Video (movies, clips)
“This data is not neatly arranged — it’s like a messy collection of human-created information.”
Step 2 – The GenAI Model (The Brain)
GenAI Model = The AI system that learns patterns
“This is the core of Generative AI.
It looks at all that unstructured data and learns patterns and relationships inside it.”
What does ‘learning patterns’ mean?
- In text → learns grammar, meaning, style
- In images → learns shapes, colors, and objects
- In audio → learns rhythm and sound patterns
It doesn’t memorize — it generalizes.
“The AI doesn’t store the exact sentences or pictures.
It understands how words, images, or sounds usually appear together.”
Example:
If trained on text:
It learns that words like “good” often appear near “morning” —
so when you say “good…”, it predicts “morning”.
If trained on images:
It learns that cats often have ears, whiskers, and tails —
so it can draw a new cat that looks realistic, even if it never saw that exact cat.
In short:
“GenAI learns the patterns and distribution of data —
how often certain things occur together.”
Step 3 – Output: New Content
🟩 New Content (Output)
“Once the GenAI model has learned, it can now create new data that follows those patterns.”
Example outputs
| Type | What it creates |
| Text | Essays, poems, code, summaries (like ChatGPT) |
| Image | Artwork, product designs (like DALL·E or Midjourney) |
| Audio | Music, voice (like Suno AI) |
| Video | Short clips or animations |
The output looks original — but it’s based on what the model has learned from data.
Generative AI first takes in lots of unstructured data (like books or images).
Then, it learns the patterns and relationships inside that data.
Finally, it uses what it learned to create new content —
like text, images, or music — that follows the same style.
Examples
Example 1: Text (ChatGPT)
- Input: Millions of articles, books, and conversations.
- Learns: Grammar, word meanings, sentence patterns.
- Output: New sentences or essays that sound natural.
Example 2: Image (DALL·E)
- Input: Millions of labeled images.
- Learns: How objects look and combine (e.g., “dog”, “hat”, “beach”).
- Output: A new image — “a dog wearing sunglasses on the beach.”
Example 3: Music AI
- Input: Thousands of songs.
- Learns: Rhythm and melody patterns.
- Output: A new song in the same style.
The easiest way to know whether a model is Generative AI or not is to look at what kind of output it produces.
If
O/P: Number, class, probability, category → Not a GenAI
Meaning:
If an AI model gives a number, label, score, or category as output —
it’s not Generative AI.
These are traditional or discriminative models — they predict something but do not create anything new.
Examples:
| Task | Output | Explanation |
| Spam detection | “Spam” / “Not Spam” | Just classifies messages |
| Face recognition | “Person A” | Identifies, doesn’t create a new face |
| Credit score prediction | “Score = 720” | Gives a number, no new data |
| Sentiment analysis | “Positive” / “Negative” | Predicts class only |
| Object detection | “There’s a cat” | Detects object, doesn’t create image |
If the AI is only choosing from known options — like yes/no, cat/dog, positive/negative —
it’s not Generative AI, because it’s not making anything new.
If
O/P: Text, Audio, Images, Video Frames → GenAI
Meaning:
If the AI model creates or generates new content, like text, sound, pictures, or video —
then it is a Generative AI.
✅ Examples:
| Task | Output | Explanation |
| Text generation | Writes essays, poems, or code | ChatGPT, Gemini |
| Image generation | Creates new artwork or designs | DALL·E, Midjourney |
| Audio generation | Produces human-like voices or music | Suno AI, Voiceflow |
| Video generation | Makes short AI videos or animations | Runway, Pika Labs |
So, Generative AI is like an artist — it doesn’t just identify things, it creates something new from patterns it has learned.
Generative AI is all about creating new content — text, images, or code — using models called LLMs (Large Language Models) like ChatGPT, Gemini, or Claude.”
Generative AI → Create content → LLM Model
Example:
“When you ask ChatGPT: ‘Write a poem about AI,’
it uses the LLM to generate new text.”
Input: Query or prompt (your question)
Output: Generated content (text, code, summary, etc.)
2️⃣ What the LLM (Large Language Model) does
“It predicts the next words based on patterns it has learned from huge amounts of data.”
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation)
Point to the pink section labeled External Source → RAG
“Sometimes, an LLM doesn’t know updated or domain-specific information.
So we combine it with external data sources like the internet or databases — this is called RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation).”
“RAG means the model retrieves real data from external sources (like a search engine) and then generates an answer using that information.”
Example:
“When ChatGPT searches the web to answer a question about 2025 events, that’s RAG in action.”
Generative AI tools use resources like search engines (DuckDuckGo) or academic sites (Arxiv) to pull external information for better responses.
Generative AI is reactive — it only works when we give it a prompt or question.
But now, AI is moving one step ahead — to Agentic AI, where the system doesn’t just respond, it can plan, take actions, and achieve goals on its own.
