🎯 From Remembering to Dreaming — Meet the Goal-Based Agent!
So far, we’ve met two types of agents:
- One that reacts instantly like a robot with no memory (Simple Reflex Agent 🤖).
- Another that remembers what just happened (Model-Based Agent 🧠).
But now… meet the motivated one — the Goal-Based Agent — the one that actually wants something in life! 😄
If the previous agents were like “Okay, I’ll just do what I always do,” this one says —
“Wait a second… what do I want to achieve here?” 🎯
Yes, this is the ambitious agent. It doesn’t just act or react; it plans its actions to reach a goal — just like students planning to pass their exams (or at least trying to 😜).
So let’s dive into how this agent thinks, plans, and works smarter — not harder!
A Goal-Based Agent doesn’t just react to what it senses — it thinks ahead before acting.
It chooses actions based on goals — i.e., what it wants to achieve.
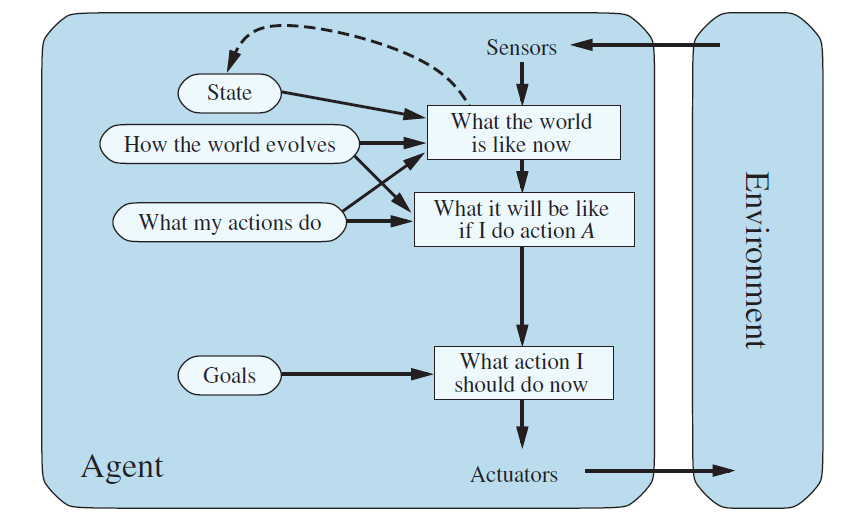
In the diagram, the environment sends information to the agent through sensors. The agent observes the world and decides its next action using reasoning and planning. Let’s understand the flow step by step:
1️⃣ Sensors → “What the world is like now”
The agent observes its environment through sensors (camera, GPS, etc.).
Example: Taxi senses it’s at an intersection, light is green, cars are on both sides.
2️⃣ State + Models (Memory & Knowledge)
The agent already has:
State: remembers where it was previously.
How the world evolves: knows how time and actions change the world (traffic lights turn red, cars move, etc.).
What my actions do: knows the results of its own actions (turning left → moves into new lane).
👉 These 3 together help the agent understand what’s going on right now.
3️⃣ “What it will be like if I do action A”
Now the agent predicts the future — it simulates or imagines what might happen if it performs each possible action.
Example:
- If I turn left, I’ll enter a one-way street.
- If I go straight, I’ll reach the highway.
- If I turn right, I’ll move away from my goal.
4️⃣ Goals → “What do I want to achieve?”
The agent has one or more goals that describe desired situations.
Example: “Reach the airport safely.”
5️⃣ “What action should I do now”
The agent now compares its predicted outcomes with its goals and chooses the action that moves it closest to the goal.
Example:
“To reach the airport, I should go straight.”
6️⃣ Actuators → Perform the Action
Finally, the chosen action (steering, braking, accelerating) is sent to the actuators — the physical part that interacts with the environment.
Example
Self-Driving Car:
- Sensors detect obstacles and traffic signals.
- The agent predicts what will happen if it speeds up or turns left.
- The goal is to reach the destination safely.
- The agent chooses the safest and shortest route.
