ID3 (Iterative Dichotomiser 3) is a popular algorithm used to construct a decision tree for classification problems.
It selects the best attribute for splitting the data based on Information Gain, which is calculated using Entropy.
The main goal of ID3 is to create a tree that classifies data with maximum purity at each node.
What ID3 Stands For
ID3 stands for Iterative Dichotomiser 3.
Key Idea of ID3
ID3 chooses the attribute that reduces entropy the most and makes the data as pure as possible after splitting.
Measures Used in ID3
ID3 uses the following measures:
- Entropy – to measure impurity
- Information Gain – to select the best attribute for splitting
(a) Entropy
Entropy measures the impurity or randomness in the dataset.
Formula:
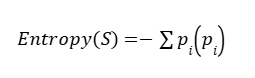
- Entropy = 0 → Pure node
- Entropy is maximum → Highly impure node
6. Information Gain Formula
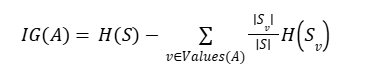
Where:
IG(S, A)
→ Information Gain of attribute A on dataset S
S
→ Complete dataset (parent/root node)
A
→ Attribute (feature) used for splitting
H(S)
→ Entropy of the dataset before splitting
Values(A)
→ All possible values of attribute A
v
→ A specific value of attribute A
Sᵥ
→ Subset of dataset S where attribute A = v
|S|
→ Total number of samples in dataset S
|Sᵥ|
→ Number of samples in subset Sᵥ
|Sᵥ| / |S|
→ Weight of subset Sᵥ
H(Sᵥ)
→ Entropy of subset Sᵥ after splitting
∑ (summation)
→ Sum of weighted entropies of all subsets
Algorithm Steps of ID3
ID3 Algorithm Steps
- Calculate the entropy of the dataset.
- For each attribute, calculate the Information Gain.
- Select the attribute with the highest Information Gain as the root node.
- Split the dataset based on the selected attribute.
- Repeat the process recursively for each child node.
- Stop when:
- All samples belong to the same class, or
- No attributes are left for splitting.
Characteristics of ID3
Suitable for multiclass classification
Uses Entropy & Information Gain
Mainly used for classification
Works best with categorical data
Can split a node into more than two branches
