Reinforcement Learning (RL)
- Definition:
Reinforcement Learning is a type of machine learning where an agent interacts with an environment to learn how to perform tasks.
- Process:
The agent takes actions —
Rewards for good outcomes
Penalties for bad outcomes
- Goal:
Over time, the model learns which actions lead to the best rewards through experience.
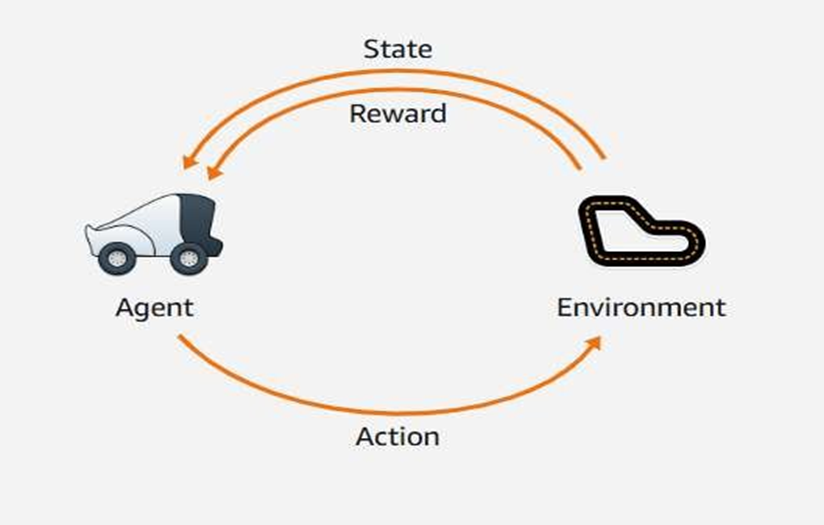
How Does AWS DeepRacer Learn to Drive by Itself?
- In Reinforcement Learning, an agent (the car) interacts with an environment (the track) to maximize rewards.
- The car observes the current situation (state) and decides an action — such as turning or moving forward.
- The environment then gives feedback (reward) based on how good that action was.
- Through trial and error, the car learns which actions help it stay on track and earn higher rewards over time.
- This process helps AWS DeepRacer learn driving skills automatically — without human control.
Agent
Think of the agent as the “brain” of the car.
- In AWS DeepRacer, the agent is like the virtual driver that learns how to drive the car inside a computer simulation.
- It looks at what’s happening around it — for example, where
the track is or if there’s a turn ahead — these are its inputs.
- Based on those inputs, the agent decides what to do next —
go straight, turn left, or turn right — these are its actions.
- Over time, it learns which actions help the car stay on track
and earn more rewards.
- In short:
The agent = the car’s learning brain that takes in information
and makes driving decisions.
Environment
Think of the environment as the “world” where the car
learns to drive.
- In AWS DeepRacer, the environment is the track on which the car drives.
- It defines where the car can go (the path) and what situations
it can face — for example, straight roads, curves, or turns.
- The car (agent) keeps driving around this track, exploring
different situations.
- While doing this, it collects data that helps its neural network
learn how to drive better.
- In short:
The environment is like a playground or practice area where
the car learns by trying out different moves.
️ State

Think of a state as a picture or moment in time for the car.
- A state shows what the car (agent) sees right now on the
track.
- It’s like taking a snapshot of the road — where the car is, how
the track looks, and what’s ahead.
- In AWS DeepRacer, the car has a front camera that captures
this image — that’s its state.
- The car uses this image to decide what to do next — whether to go straight or turn.
- In short:
A state = What the car sees at one moment while driving.
Action

Think of an action as the car’s next move.
- After the car (agent) sees the road — that’s its state — it has
to decide what to do next.
- The action is that decision:
→ Should it turn left, turn right, or go straight?
→ Should it go fast or slow down?
- In AWS DeepRacer, each action means driving at a specific
speed (throttle) and steering angle (direction).
- In short:
An action = The car’s move based on what it sees.
Reward

Think of a reward as the car’s score or feedback.
- When the car (agent) takes an action, it gets feedback from the environment.
- If the car does something good (like staying on the track or driving smoothly), it gets a high reward.
- If it does something bad (like going off the track or crashing), it
gets a low reward or no reward.
The reward helps the car learn which actions are good and
which are not.
Over time, it tries to take actions that earn more rewards —
that’s how it learns to drive better.
- In short:
A reward = Points or feedback that tell the car how well it’s
doing.
How to train a reinforcement learning model.
Training an RL Model
➵ Think of training like practicing again and again until you
get better.
- In Reinforcement Learning, the agent (car) keeps trying
different actions in the environment (track).
- Each time it drives, it learns from its experience — what
worked well and what didn’t.
- All these experiences are used to update its brain (neural
network) so it can make smarter decisions next time.
- The car keeps repeating this process — try → get feedback → improve — again and again.
In AWS DeepRacer, this training helps the car slowly learn
how to drive by itself, without human help.
- In short:
The car learns by practicing, just like a student learning a new
skill through trial and error.
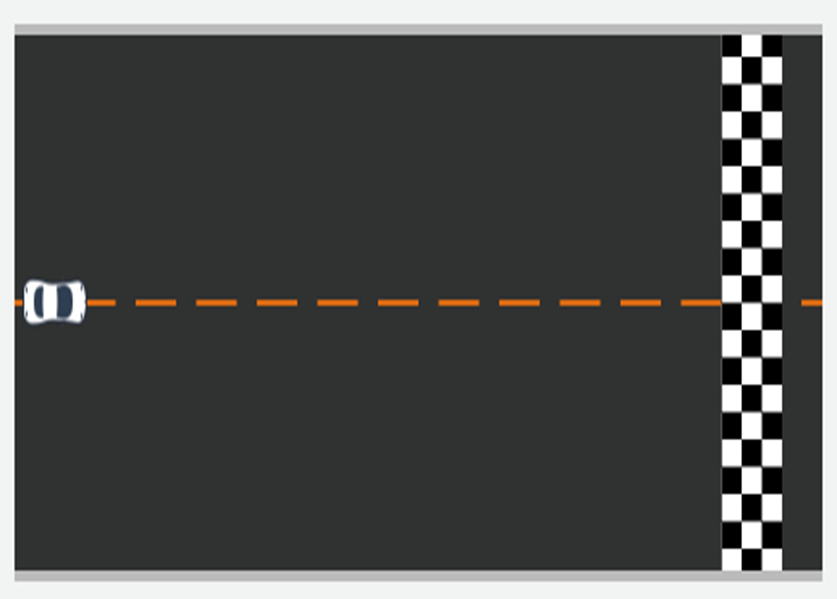
Think of this like a simple board game for the car.
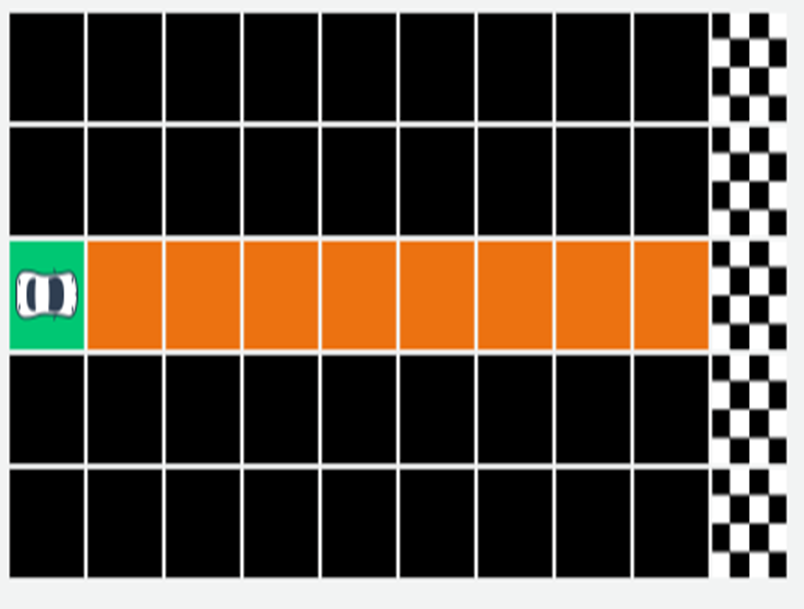
- The car starts on the green square (start) and must reach the
checkered flag (finish).
- The grid is like the car’s world (environment), divided into small boxes called states.
- The car can move one step at a time — either forward, up, or down — to reach the goal.
- The shortest path means the car should reach the finish line
using the fewest moves possible.
- During this process, the car learns which moves help it reach
faster (good actions) and which moves don’t (bad actions).
- In short:
This simple grid helps show how the car learns to plan its path step-by-step — just like you learn the best route to your classroom!
Scores
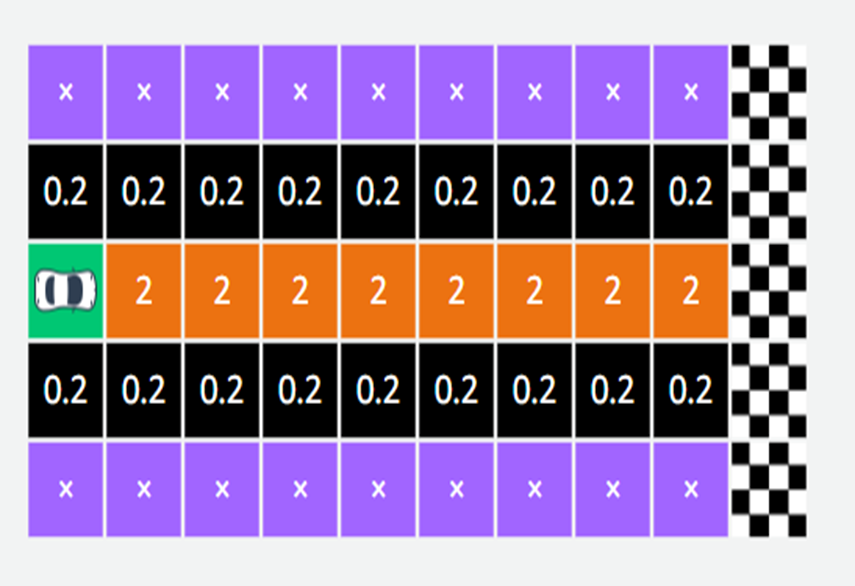
Imagine our racetrack is made up of small boxes (like a grid). Each box can have a score, which tells the car whether it’s doing well or not.
- The boxes in the center of the track give a high score (reward)
— this tells the car, “Good job! You’re driving correctly.”
- The boxes at the edge of the track are called stop states — if the car goes there, it gets a low score or penalty. This means, “ You went off the track.”
So, by giving high rewards for staying in the center and low
rewards for going off track,
we are teaching the car to always drive straight down the middle of the road.
An episode
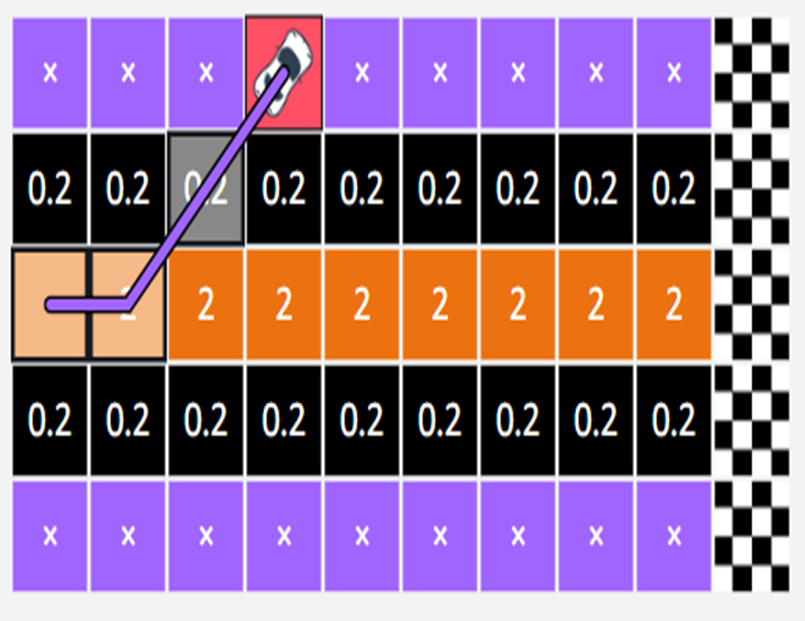
In reinforcement learning, the vehicle begins by exploring the grid. It keeps moving until it either goes outside the track or reaches the goal.
As it moves, it collects rewards based on the scores assigned to
each position.
Each time the car moves:
If it moves correctly (stays on the track), it gets some points — called a reward.
If it goes off the track, the game stops — that’s a stop state
(the car failed that round).
Now, one full attempt by the car — from the start until it either
finishes or fails — is called an episode. So, in this example:
The car started moving,
Collected rewards as it moved along (for good moves),
And before it went off the track, it earned a total of 2.2 points.
Iteration
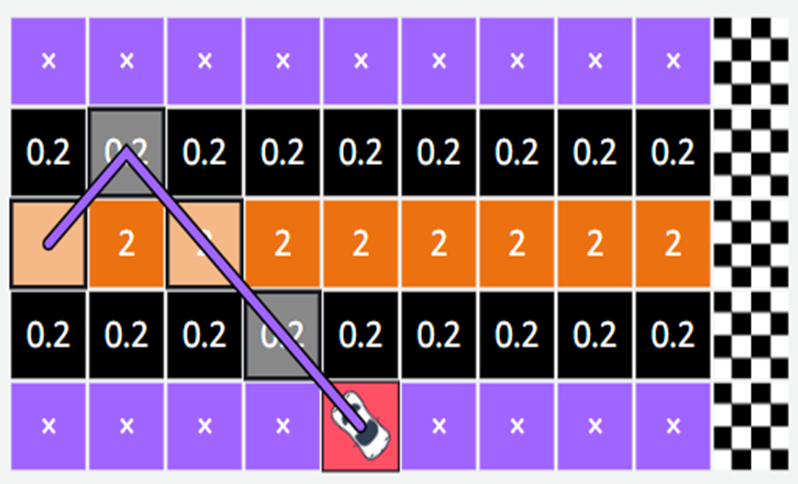
In reinforcement learning, the computer (or agent) doesn’t
learn everything in one try.
It learns step by step — by repeating the process many times. Each time, it tries different moves (called actions) and notes which ones help it reach the goal and earn more rewards.
At first, the agent just explores — it tests out different paths to
see what happens.
Later, once it understands which actions work best, it uses that
knowledge to perform better and reach the goal faster.
Iteration = learning through repeated practice.
Exploration At the beginning, the agent (car) doesn’t know which path is best — so it has to try different routes on the track
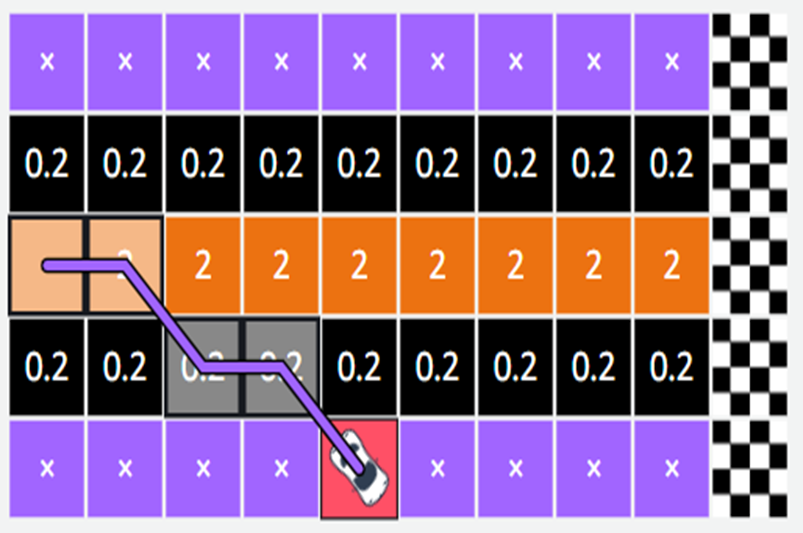
This process of trying out new moves and learning from the
results is called exploration.
As it gains more experience, it starts to figure out that staying
in the center of the track gives higher rewards.
Slowly, the car learns to avoid the edges and stay in the middle to earn more points.
If we make a graph of the total rewards after each try (episode), we’ll see that the rewards keep increasing — showing that the car is improving over time.
- In short:
Exploration means the agent is trying different things to learn what works best.
At first, it makes mistakes — but with practice, it finds the best
path and keeps improving!
Exploitation and Convergence
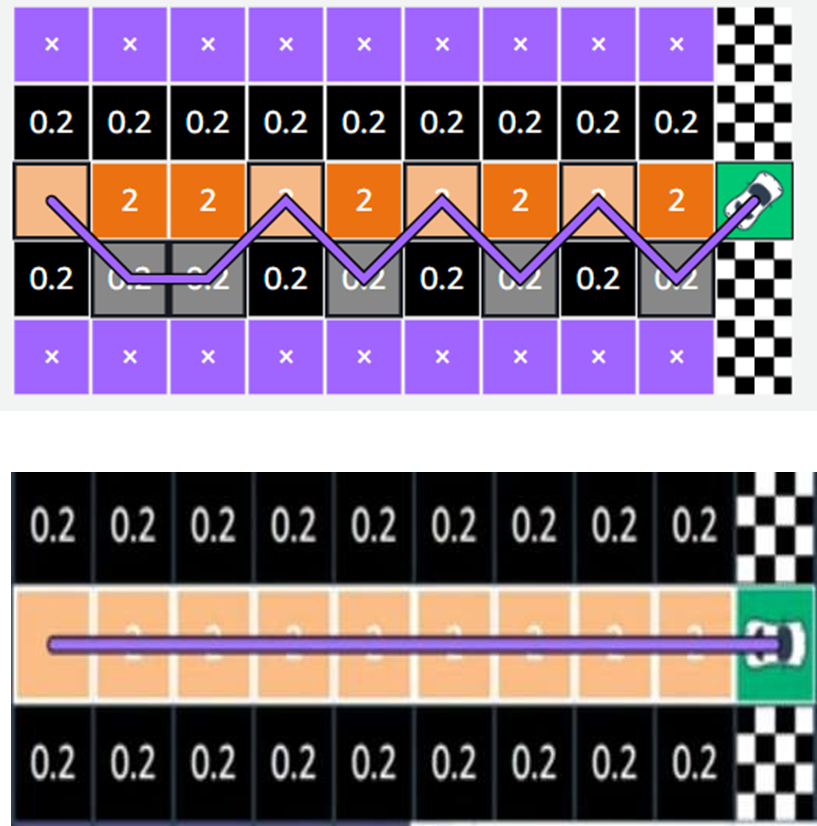
After exploring and learning from many tries (episodes), the agent starts to understand which path gives the best rewards. Now, instead of just exploring randomly, it begins to use what it has learned to reach the goal faster.
This is called exploitation — the agent is using its knowledge
to make the best possible decisions.
Over time, with more and more training, the agent becomes very consistent — it can reach the destination correctly most of the time.
This stage is called convergence, which means the learning process has stabilized, and the agent has figured out the best way to act.
In short:
Convergence → The point where the agent performs well and stops changing much — it has learned the best way!
Summary of Reinforcement Learning Steps with AWS DeepRacer
| Step | Meaning (Simple Explanation) | DeepRacer Example |
| 1. Environment | The world where the agent learns and acts. | The racetrack where the car drives. |
| 2. Agent | The learner or decision-maker in the environment. | The DeepRacer car that learns to drive. |
| 3. Actions | The possible moves the agent can take. | Turning left/right or changing speed. |
| 4. Rewards | Feedback for the agent’s actions — good or bad. | Staying in the lane = positive reward; going off-track = negative reward. |
| 5. Episode | One complete round of learning (from start to stop). | One lap around the track while collecting rewards. |
| 6. Iteration | Repeating many episodes to improve performance. | The car practices multiple times to find the best path. |
| 7. Exploration | Exploring new actions vs. using learned actions. | Tries new routes first, then uses the best route it found. |
| 8. Convergence | When learning becomes stable and performance is high. | The car drives smoothly and reaches the goal consistently. |
